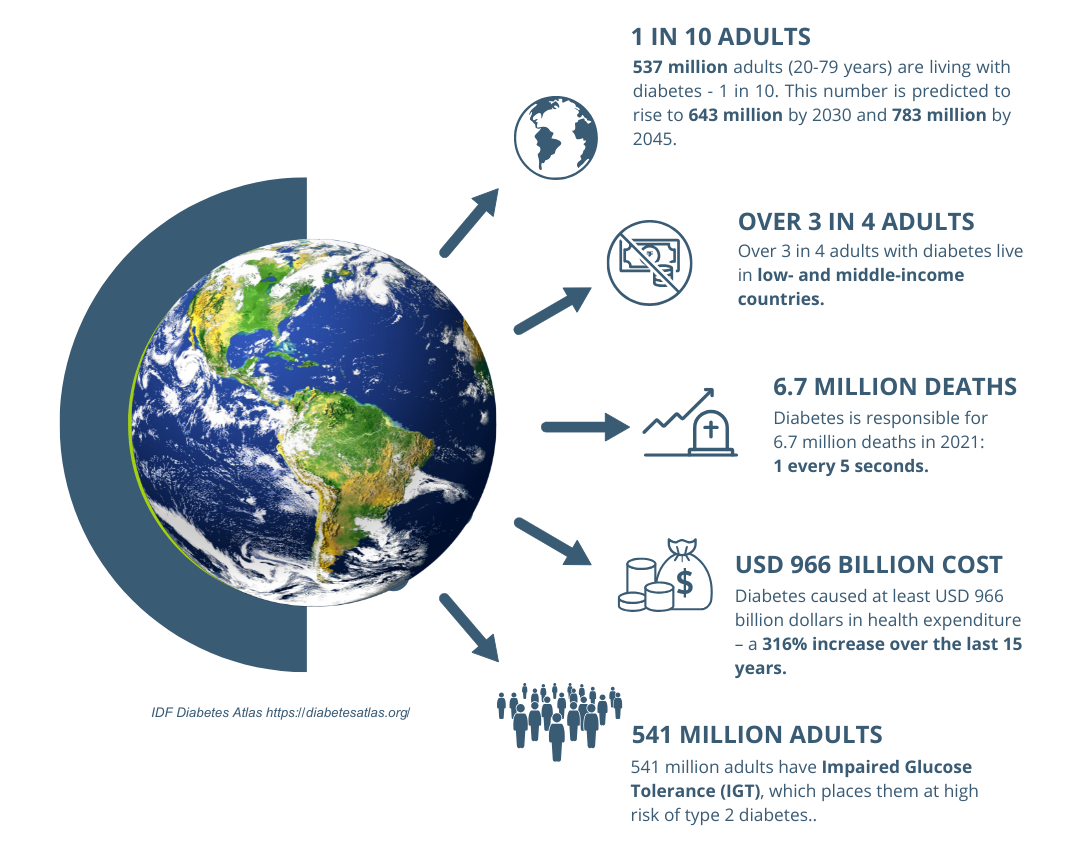
The prevalence of diabetes is escalating globally. According to the International Diabetes Federation, approximately 537 million adults are currently living with diabetes, with projections indicating this number will rise to 643 million by 2030. This increase is driven by factors such as urbanization, aging populations, and lifestyle changes.(1)
Understanding Diabetes (2)
Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs when the body cannot effectively regulate blood sugar levels. It’s characterized by chronic hyperglycemia resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. The two primary forms are:
Type 1 Diabetes (T1D): An autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. The T-cells attack pancreatic β-cells which is leading to absolute insulin deficiency.
Type 2 Diabetes (T2D): A metabolic disorder where the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough of it. It’s a multifactorial disease and often associated with obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and genetic predisposition.
Both types require careful management to prevent complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and vision loss.
Advances in Diabetes Management (3)
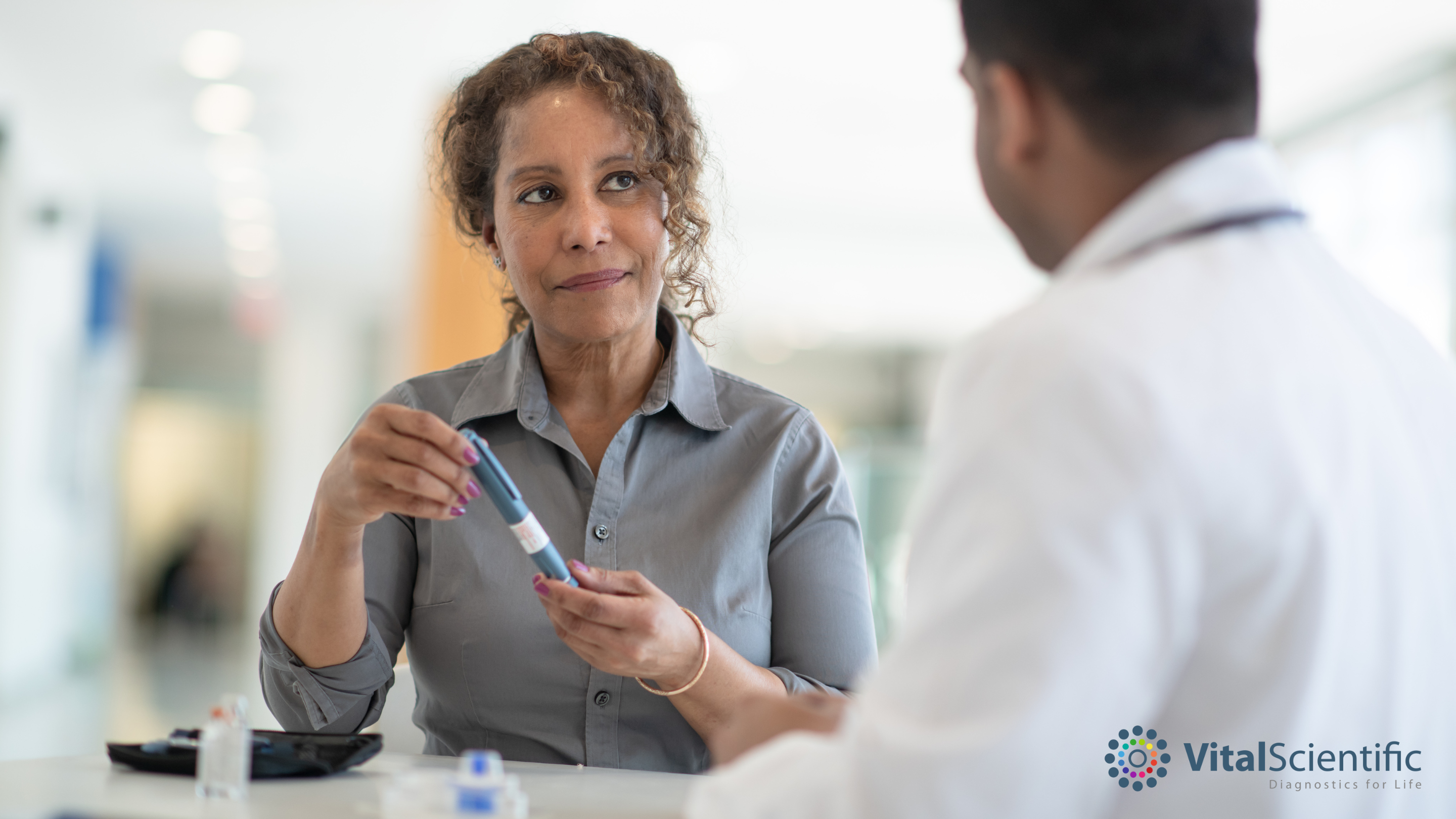
Managing diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring.
Education and Support: Understanding diabetes and having a support system can significantly improve management outcomes.
Clinical Chemistry Tests in Diabetes Management (4,5)
Clinical chemistry tests play a pivotal role in diagnosing and monitoring diabetes:
VitalScientific offers a comprehensive testing panel for Diabetes management including all key analytes: Glucose, HbA1c and Mircoalbumin. All reagents are ready-to-use liquid stable and optimized for the Selectra Family from semi-automated to fully automated benchtop chemistry analyzers.
UN Diabetes Day on 14th November is a reminder of the collective effort required to combat diabetes. By embracing scientific advancements and promoting comprehensive management strategies, we can improve outcomes for those living with diabetes and work towards a future where this condition is better understood and controlled.
For consistent, accurate, and reliable results on VitalScientific’s Selectra Family of instruments, Selectra System Reagents, Calibrators, and Controls are recommended. For more information, please visit our reagents page or contact us.
References
- The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) https://idf.org/about-diabetes/diabetes-facts-figures/ [cited 2024 Nov 6]
- The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) IDF_Atlas_10th_Edition_2021.pdf (accessed 2024 Nov 11)
- Sugandh F, Chandio M, Raveena F, et al. (August 18, 2023) Advances in the Management of Diabetes Mellitus: A Focus on Personalized Medicine. Cureus 15(8): e43697. DOI 10.7759/cureus.43697
- Philippe Gillery(October 14, 2022) HbA1c and biomarkers of diabetes mellitus in Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine: ten years after https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2022-0894 (accessed 2024, Nov, 11)
- Résimont G, Cavalier E, Radermecker RP, Delanaye P. Albuminuria in diabetic patients: how to measure it? —a narrative review. J Lab Precis Med 2022;7:4
*Product availability may be subject to regulatory requirements. Please contact your local representative for more information.
Read more articles
Let us help you
For general inquiries or technical support, please use the link to the right. Click ‘Contact’ to complete a brief online form, and someone will be in touch with you soon.